![]()
![]()

Displacement
|
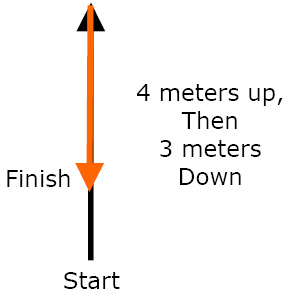
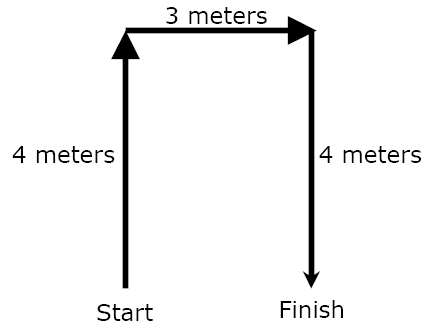
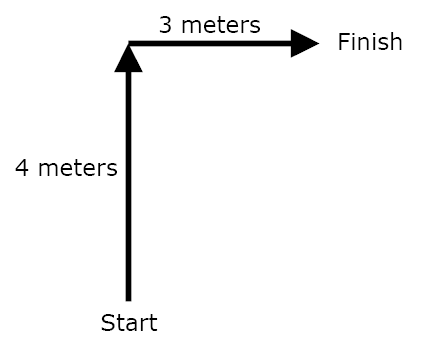
When studying motion, physicists find it more useful to measure the displacement of an object rather than the distance. Displacement refers to the object's change in position from its starting point to its finishing point, taking both distance and direction into account. How can you travel a distance of 10 meters but have a zero displacement? |
![]()
Science requires careful observations
Why does this boat float?
Ship floating on nothing! :: Physikshow Uni Bonn
School blocks YouTube? Use the file below
Sulfur hexafluoride is more dense
then the surrounding air
When physicists study motion they study
displacement
not distance.
Video Instruction
showmethephysics.com
|
Enduring Understanding 1. Displacement is an oject's distance and direction traveled from start to finish. (What happens in between doesn't matter) 2. + is up, right, east and forward.
|
C. Displacement - distance & direction from start to finish
1) Examples
|
Displacement? |
1 m up
|
Displacement? |
3 m Right
(Start to finish)
|
Distance = 7 meters
Displacement =
5 m N of E |
2) Displacement always has ...
Magnitude
(a number)

..and direction

a) Examples
• 5m East
• 7m upward
• + 17 m
b) Positive and Negative Signs also show direction

+ Usually up, right, north, east, forward
- Usually down, left, south, west, backwards
c) Symbol for displacement: d
Summary Review
 |
At what point is
1) greatest? |
[ Flash ]
4) What is the displacement at C?

 |
1) B 2) At the start 3) Any point between |
 |
|
![]()
 |
Velocity AP |
 |
![]()
©Tony Mangiacapre.,
- All Rights Reserved [Home]
Established
1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)