Physics Java on the Web
|
Electricity |
|
Magnetism |
|
BEFORE
YOU BEGIN: Highlight the questions you were assigned, |
||
Electrostatics
Charges and Fields - Part I
In which general direction do all the electric field lines point near the positive charge?
________________________________________________________________________
near the negative charge? ____________________
Where is the electric field strongest?
________________________________________________________________________
What is the geometric shape of the field between the charges? Click many times in this area until the pattern is clear.
________________________________________________________________________
Charges and Fields Part II
Move the small yellow charges around each charge. What do you think it means when the arrows get bigger as you move the small charges near the bigger charge?
________________________________________________________________________
Is the yellow charge positive of negative? __________
Explain your answer.
________________________________________________________________________
Current Electricity
|
BEFORE YOU BEGIN: Highlight the questions you were assigned, choose FILE, PRINT, SELECTION, PRINT |
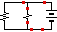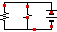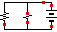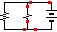
Electric Circuit Activity IMPORTANT - Scroll down to the SECOND circuit on this page where it says "Procedure for Series Circuit"
Series Circuit
Series circuits and voltage
DIRECTIONS: 1) Close the circuit with your mouse (purple switch) 2) Press SHOW VOLTAGES.
1. List the resistance values of the 3 bulbs originally in the circuit. R = __________ R = __________ R = __________
2. What are the voltages of each of these bulbs? V = ________ V = ________ V = ________
3. How does the sum of the light bulbs voltages compare with the batteries voltage?
________________________________________________________________________
4. Drag and drop new light bulbs on top of the existing light bulbs. How does the sum of the voltages of the new light bulbs compare with the batteries voltage?
________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the relationship between the size of the resistance of the bulbs and their brightness? (Experiment with different bulb arrangements)
________________________________________________________________________
Series Circuits and Current
DIRECTIONS: 1) Close the circuit with your mouse (purple switch)
2) Press SHOW CURRENTS and press HIDE VOLTAGES (make sure the circuit is closed)
6. What do you notice about the current going through each resistor?
________________________________________________________________________
7 Vary the bulbs in the circuits. What conclusion can you make about the size of the total resistance and the size of the total current in a series circuit?
________________________________________________________________________
Parallel Circuit (Scroll DOWN a little)
DIRECTIONS: Close the circuit with your mouse (purple switch)
b) Choose HIDE VOLTAGE and SHOW CURRENT
8. Compare the size of the current going INTO the whole middle branch (two bulbs connected in parallel) with the SUM of the current in EACH bulb in the middle branch.
_________________________________________________________________________________
9. Drag and drop different size bulbs on to the middle branch. a) Compare the brightness of the low resistance bulbs with the brightness of the high resistance bulbs.
_________________________________________________________________________________
b) What is the relationship between the size of the resistors in the middle branch and their current.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Ohm's Law - University of Oregon
1. How much resistance must be placed into this circuit to make the light bulb light with the 12 volt battery?
a) how much resistance for the 6? ________ 18? ________ 24? ________
2. Determine the amperage (current) of the light bulb.
Magnetism - Check these out