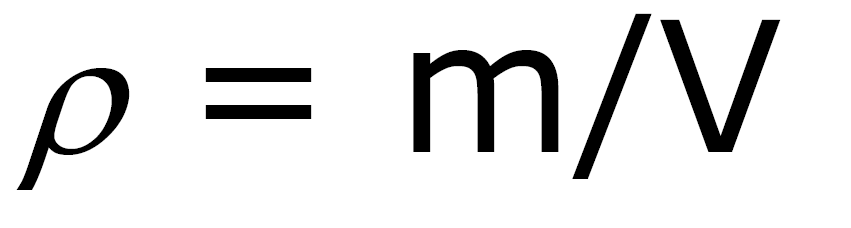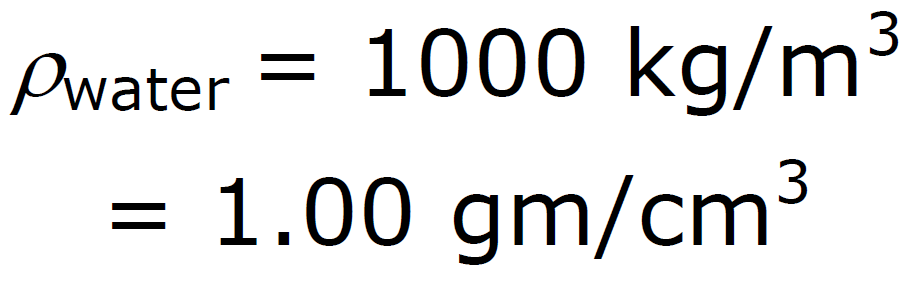
Fluid: a substance that has definite mass but not definite shape.
Ex: gases and liquids Density: mass/volume
ρ Units: ρ water = 1 g / cm3 =
__________kg/m2 = __________Kg/L
Weight of a Fluid – force gravity exerts on a fluid = mg
Equation:
Specific Gravity - density of a fluid compared to the density of water.
Specific Gravity - comparison of the density of a substance with the density of water
| Specific Gravity | = |
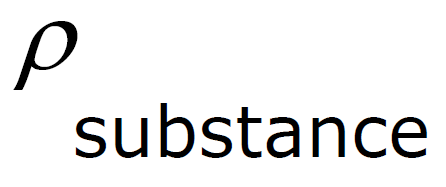 |
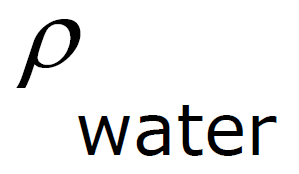 |
Alcohol or lead, which has a specific gravity of 11?
![]()
Pressure = F/A
N/m2 or Pascal
Pressure under a Liquid
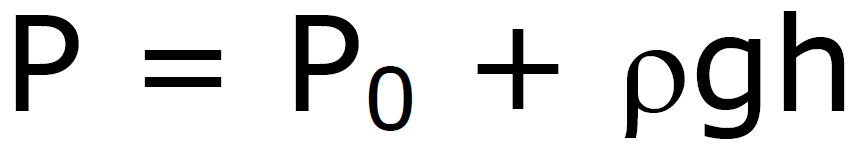
P0 –
pressure above liquid
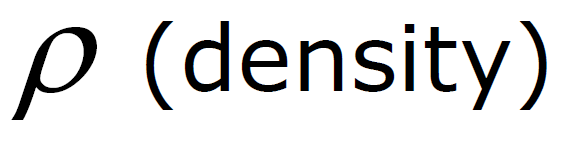
(Density in liq. depends only on h)
![]()
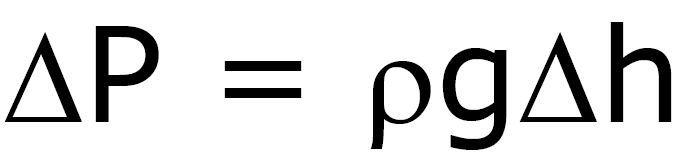
(Density depends only on h)
P0
– pressure above liquid
at sea level
1 atm = 1.013 x 105 N/m2
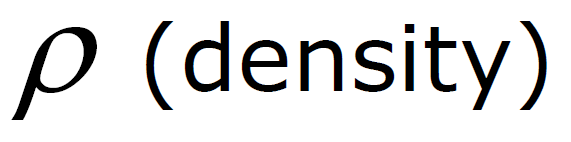
![]()
Pascal’s Principle
If a force is applied on one place in an enclosed liquid the pressure
increases everywhere else in the liquid.
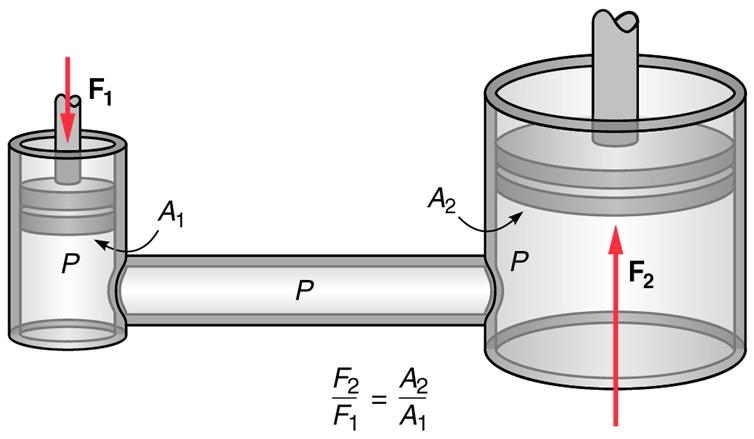
| F2 | = | A2 |
| F1 | A1 |
Giancoli p. 281) 14, 16
density of water = 1000 kg/m3
![]()
Buoyancy
"Archimedes Principle"
Why do some substances float in a liquid and some sink?
Objects that are less dense than the liquid sink.

The buoyancy force produced by a liquid is equal to the weight of the volume displaced

FB= Weight of fluid displaced= Weight of fluid displaced
FB = mg
Buoyancy force = submerged weight
(rfluid)(Vsubmerged)g
(rfluid)(Vsubmerged)
![]()
Gauge Pressure - fluid pressure w/o atmospheric pressure
Absolute Pressure - fluid pressure with atmospheric pressure
![]()
Apparent Mass or Weight
- mass or weight in fluid
| mg - | mg | = | rVg |
|
weight in air |
(apparent mass or weight) |
Mass of liquid displaced |
V of liquid displaced
= V of object submerged
![]()
Density / Part Submerged
| Density | Part Submerged |
| 800 kg/m3 | 8/10 submerged |
| 250 kg/m3 |
1/4 submerged |
| SG = .75 |
3/5 submerged |
125 kg/m3 |
1/8 submerged Density? |
![]()
Partially Submerged /
Density and SG
| Apparent Mass or Weight in Liquid |
= | SG |
| Mass or Weight in Air |
![]()

![]()
©Tony Mangiacapre., St. Mary's H.S., Manhasset,
NY
All Rights Reserved [Home]
Established 1995