![]()
 Home
Home
![]()
Try this at home!
Egg trick learn how now
PE and k
e) PEs in terms of k - Ideal Spring
1. P.E.s = Fx
Average Force: F = F/2
2. PE = (F/2)x
substitute F = Kx (On reference)
3. P.E.s = (1/2)(Kx)x
| P.E.s = 1/2(kx2) |
(On reference)
|
Ex 1) A force of 12. N stretches a spring and makes it .15m longer
a) What the spring constant (k) of this spring? |

Ex 1) A force of 12. N stretches a spring and makes it .15m longer
a) What's the spring constant (k) of this spring?
k = F/x
= 12. N/.15 m
= 80. N/m
b) P.E. of this spring?
PEs = (½)Kx2
= 1/2(80. N/m)(.15 m2)
Be sure to use parenthesis when calculating!!
PEs = .90 Joules

|
Ex 2) If 15. joules of energy are stored in the stretched spring below, what is the value of the spring constant? |
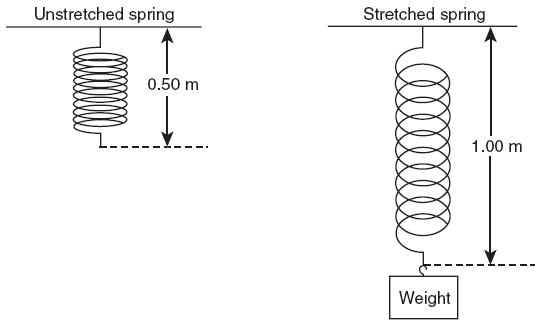
Ex 2) If 15. joules of energy are stored in the stretched spring, what is the value of the spring constant

| P.E.s = 1/2(kx2) |
15. J = (½)k(.50 m2)
1/2 in decimal form is .50
15. J = .50 k(.25)
15 = .125 k
Divide both sides by .125
k = 120 N/m
![]()
|
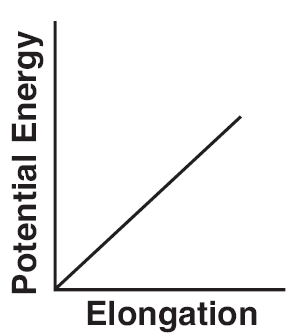
What's wrong with this picture?
P.E.s = (1/2)kx2 x = elongation
P.E.s = 1/2(kx2) PE, X direct square Plot should be curved |
W = DPE
29) A 1200 kg car rolling on a horizontal surface has a v = 65 km/hr when it strikes a horizontal coiled spring and is brought to rest in a distance of 2.2 m.
What is the spring constant of the spring?
DKE = DPE
65 km/hr x [1000m/km][1hr/3600]
= 18 m/s
1/2mv2 = 1/2kx2
mv2 = kx2
mv2/[x2] = k
8.1 x 104 N/m
![]()
![]()
©Tony Mangiacapre., -All Rights Reserved
[Home]
Established 1995
Use any
material on this site (w/ attribution)