![]()
![]()
Temperature and Current - MIT TV
 |
"Why does the bulb get brighter when the rod is put in the liquid nitrogen?" |
 |
"Lowering the temperature of a wire reduces resistance and increases current" |
Show Me
The Physics
YouTube Channel
II. Circuit Concepts
Conservation of charge and energy for electric current

Gustav Robert Kirchhoff
(March 12, 1824 – October 17, 1887) was a German physicist
This image is in the public domain because its copyright has expired.
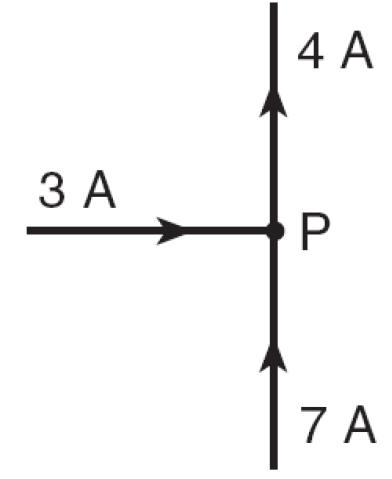
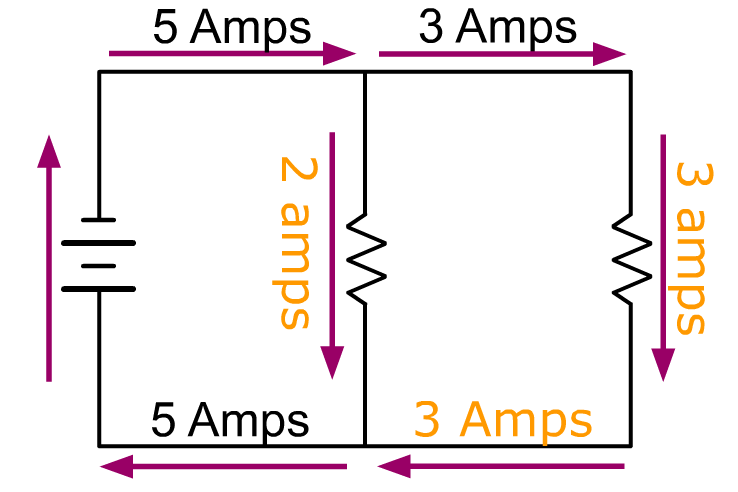
1) Kirchhoff's 1st Law
| Total
current arriving at a point in a circuit = Total current leaving the point. (Conservation of Charge) |
“Amps In = Amps Out”



Ex 1)




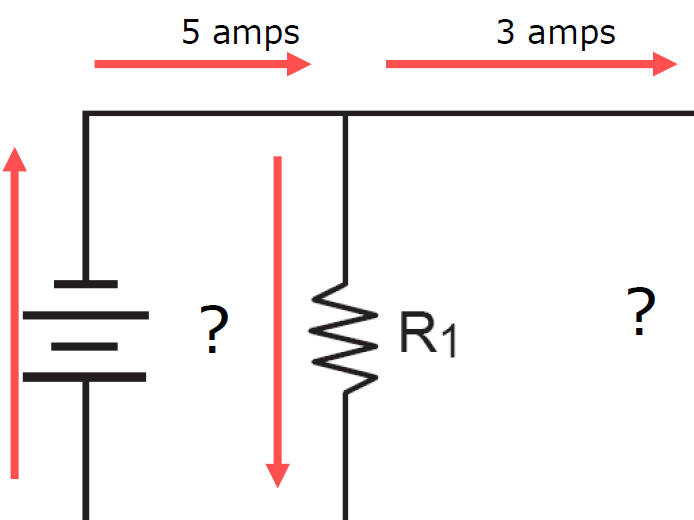
Amps In = Amps Out
5 Amps = 3 Amps + x
X = 2 amps






Remember
“Amps In =
Amps Out”



Ex 2) Current in bottom branch?
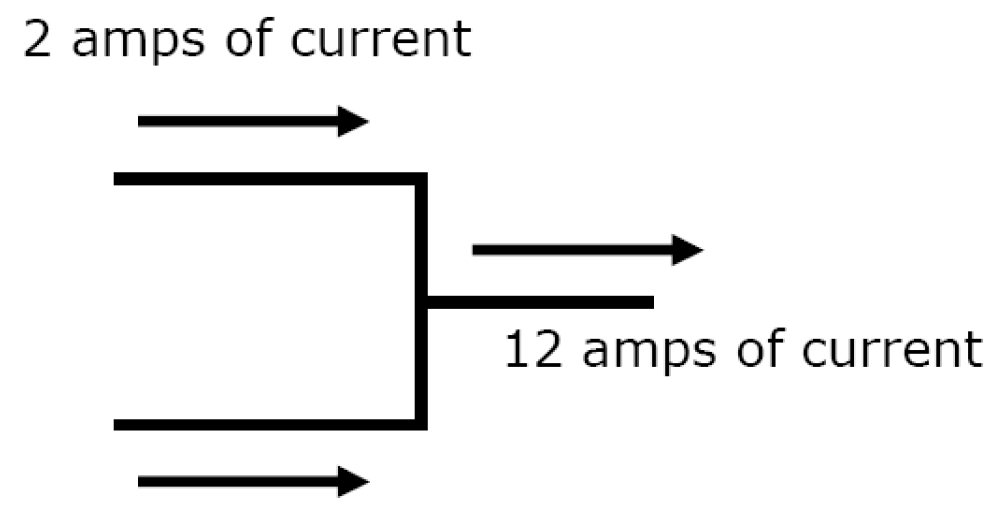
Amps In = Amps Out
| 2 Amps + X | = | 12 Amps |
X = 10 amps



Ex 3)
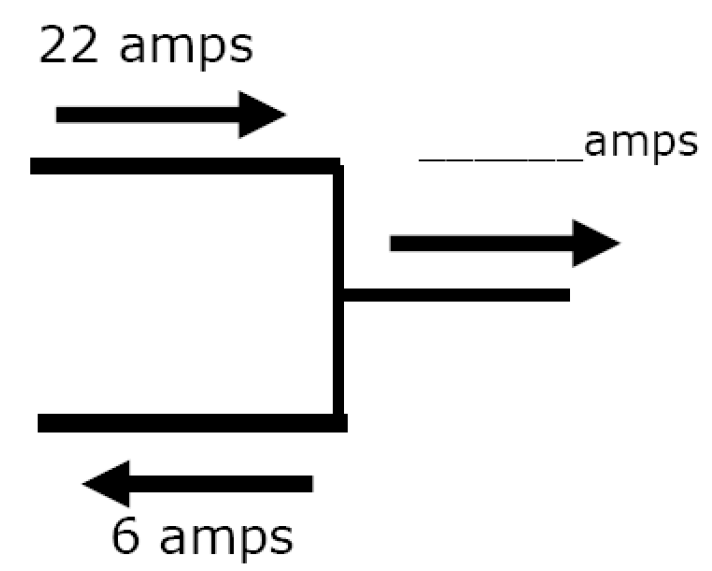
Amps In = Amps Out
| 22 Amps | = | x Amps + 6 Amps |
X = 16 amps



Ex 4)
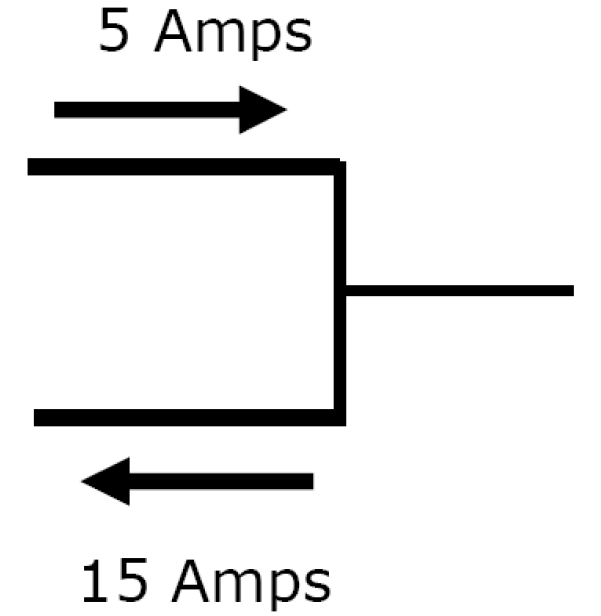
Amps In = Amps Out
5 A + x = 15 A
x = 10 A IN



|
Current In (10 A),
|



2) Kirchhoff's 2nd Law - the algebraic sum of all the voltage drops and applied voltages around a circuit = 0
(conservation of energy)
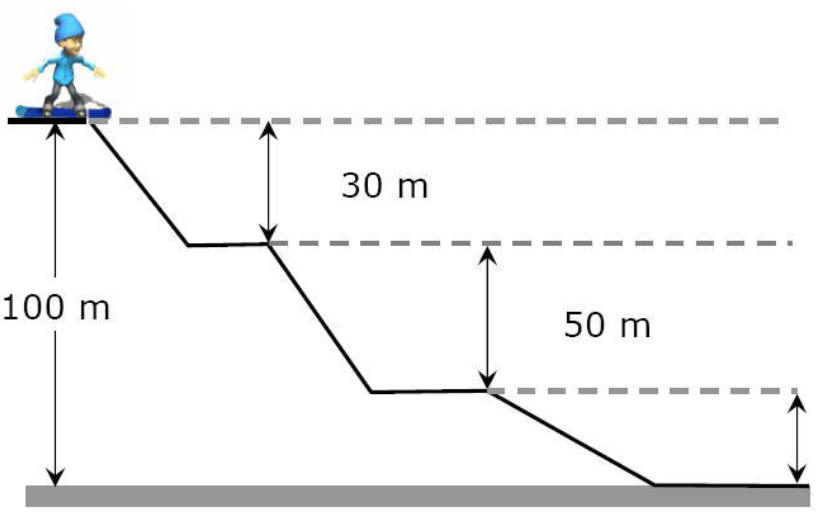
Amount of PE gained
when you go up a ski slope = energy released
going down a ski slope
(KE, Work against friction and snow)



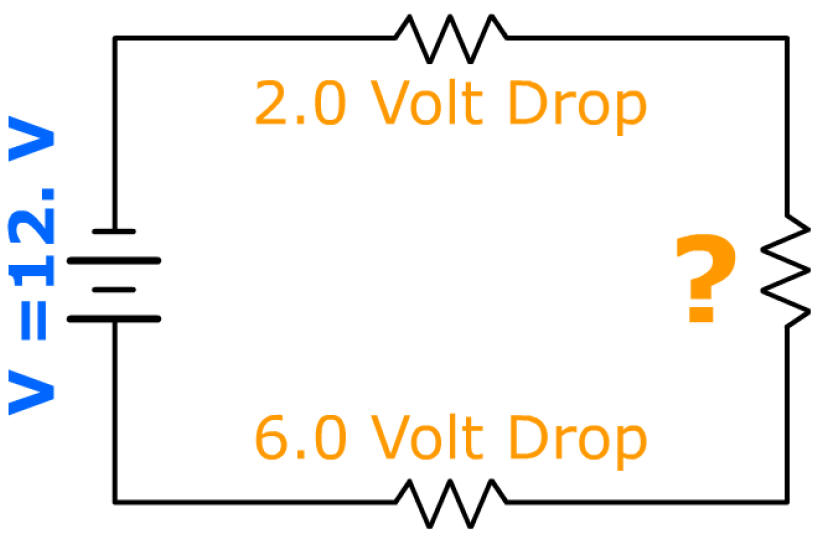
Applied Voltage
( + )
Voltage Drop
( - )
0 = 12 V + -2 V + x + -6 V
0 = 12 V + -8 V + x
0 = 4 V + x
x = - 4 volts
| VT = V1 + V2 + ... |
![]()
![]()
©Tony Mangiacapre., - All Rights Reserved [Home]
Established 1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)