![]()
 |
 |
![]()

Phonebook Friction - Mythbusters
School Blocks YouTube? Download the file below.
Ranking Task
Rank the friction on the 1.0 kg from greatest to least
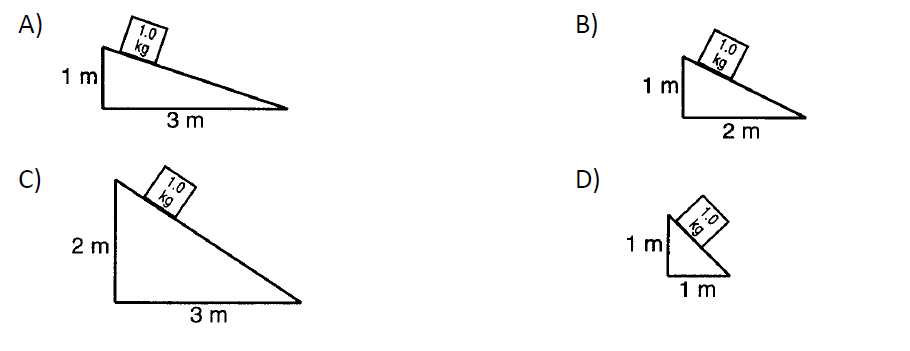
FRICTION PROBLEMS

|
*Remember |
|
Ex) A 5.0 kg Steel block is resting on a *horizontal table*. The coefficient of static friction (us) is 0.75 and the uk is 0.57 a) Minimum force is needed to start this block moving (fs)? |
Ex) A 5.0 kg Steel block is resting on a *horizontal table*. The coefficient of static friction (us) is 0.75 and the uk is 0.57.
a) What minimum force is needed to start this block moving?
fs= Fnus = Fgus = mgus
fs = mgus
= 5.0 kg(9.8 m/s2)(.75)
= 37. N
b) What is the frictional force on this object as it moves?
fk = mguk
= 5.0 kg(9.8 m/s2)(.57)
= 28 N
c) What force must be applied to the object to keep it moving at constant velocity? (Hint: Fnet = 0)
At Constant velocity
F applied = friction force
= 28 N
Friction Questions
Coefficients of Friction & F = ma
Remember ...
Static Friction fs = UsFn
Kinetic Friction fk = UkFn

|
On Horizontal Surface fs = usFg (force to start object moving) fk = ukW AND W = mg |
|
Ex 1) A 1000. N car skids on a wet concrete road. If the road is horizontal, what is the friction force on the car? |
Ex 1) A 1000. N car skids on a wet concrete road. If the road is horizontal, what is the friction force on the car?
w = 1000. N
Uk = .58
fk =
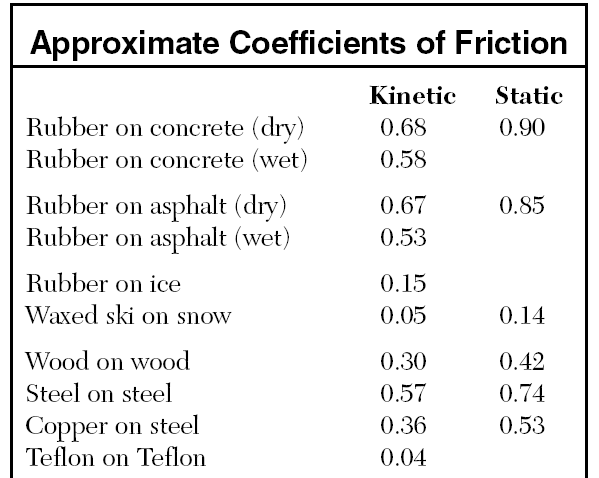
fk = UkFg = .58 x 1000. N
= 5.8 x 102 N
|
Ex 2) A skier is being pulled along a
horizontal surface at constant speed with a force of 50. N.
What is the weight of the skier? |
Ex 2) A skier is being pulled along a horizontal surface at constant speed with a force of 50. N.
What is the weight of the skier?
At constant speed:
fk = Applied Force
fk = 50. N
w = ?
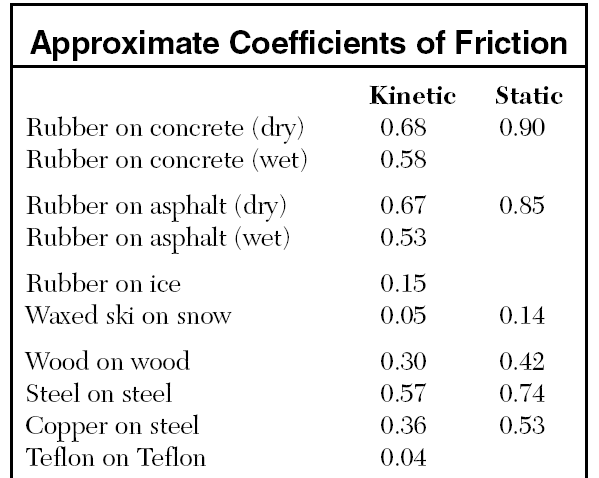
uk = .05
fk =ukFg
50. N = .05[Fg]
w = 1000 N
|
Ex 3) A 10. kg block of wood
sliding on a horizontal wooden table is brought to rest. |
Ex 3) A 10.
kg block of
wood sliding on a horizontal
wooden table is
brought to rest.
What is the
force on the block of wood that
caused it to stop?
The force of kinetic friction
stops the block.
fk = ?

Uk = .30
fk = Fnuk = Fguk = mguk
fk = mguk
fk
= (10. kg)(9.8 m/s2).30 = 29. N
|
Ex 4) A 53. kg block, slowed by friction, has an acceleration of -0.10 m/s2. What is the force of friction on the block? |
Ex 4) A 53. kg block, slowed by friction, has an acceleration of -0.1 m/s2. What is the force of friction on the block?
m = 53. kg
a = -.10 m/s2
fk = F = ma
fk=F = 53. kg(-.10 m/s2)
= -5.3 N
|
Ex 5) A force of 8.0 N gives a 3.0 kg mass an
acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 to the right.
What is the friction on the block? |
Ex 5)
A force of 8.0 N gives
a
3.0 kg
mass an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2
to the
right.
What is the
friction on the block?
Fapplied
= 8.0 N Right
m = 3.0 kg
a = 2.0 m/s2 Right
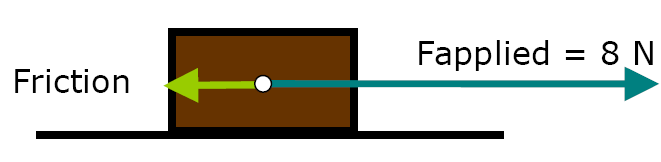
Fnet = ma = 3.0 kg(2.0 m/s2 )
= 6.0 N
What friction force will produce a net force of 6.0 N?
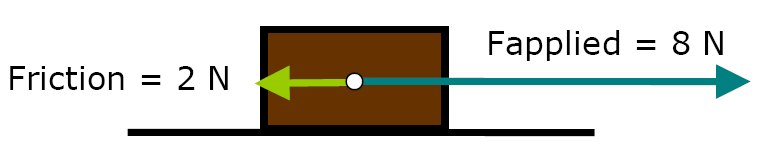
friction = 2 N left
![]()
How does the magnitude of the friction force
on a box
on a ramp change when the angle
of the ramp increases?
![]()
Friction decreases because the
normal force decreases
Review - Which law of motion best explains this?
School Blocks YouTube? Download the file below.
3rd Law of Motion - Action/Reaction
Review
Friction Video - Georgia Pacific Broadcasting
![]()
***AP Pulleys***
![]()
![]()
![]()
ŠTony Mangiacapre., - All Rights Reserved
[Home]
Established 1995
Use any material on this site (w/ attribution)