Series and Parallel Circuits Handout PART 2
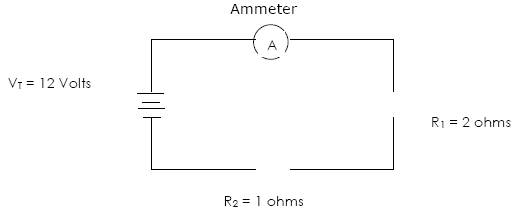
Example 6) Series Circuit

a) Find the equivalent resistance RT
b) Find the current (IT) going through this circuit
VT = IT RT
c) Find potential drop across R1 and R2
V = I R
V1 =
V =
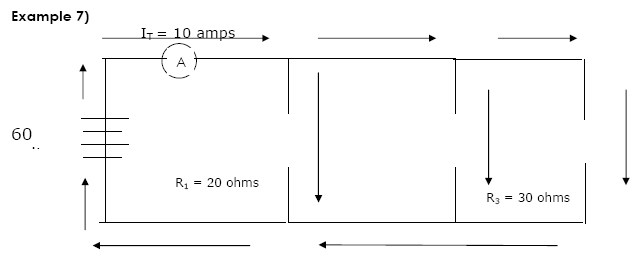
a) Find the combined resistance ( RT )
b) Find the current in R1
c) Find I3
In a series circuit: The potential drop (V)
across a resistor is proportional to resistance
Example 8)
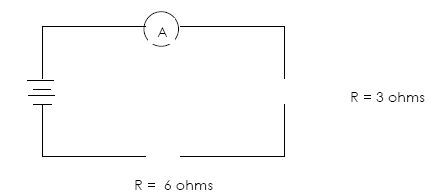
If the voltage drop across the 3 ohms resistor is 4
volts then the voltage drop
across the 6 ohm resistor is _________ volts
a) Find the total voltage in this series circuit ________
b) Find the combined resistance in this circuit ________
c) Find the total current in this circuit _________
II) Electric Power
Power - time rate of doing work or expending energy
(watts ) P = W (J)/ t (seconds)
since V = W/q , CROSS MULTIPLY then W
= _____
SUBSTITUTE *** P = Vq/ t = ____________________
All these equations are in the reference table
P = VI since V = IR …. THEN P = _______ since I = V/R …
THEN P = _________________
Electric Energy and Heat
(W) Electric energy consumed or released
as heat
All these equations are in the reference table
(J) W ____________________________________